Here is the overall structure of an experiment on a micro-chemical chip. The following components are essential:
1, A micro-chemical chip
2, A chip holder
3, Connectors for the holder
4, Capillary tubes
5, Sample-delivery devices
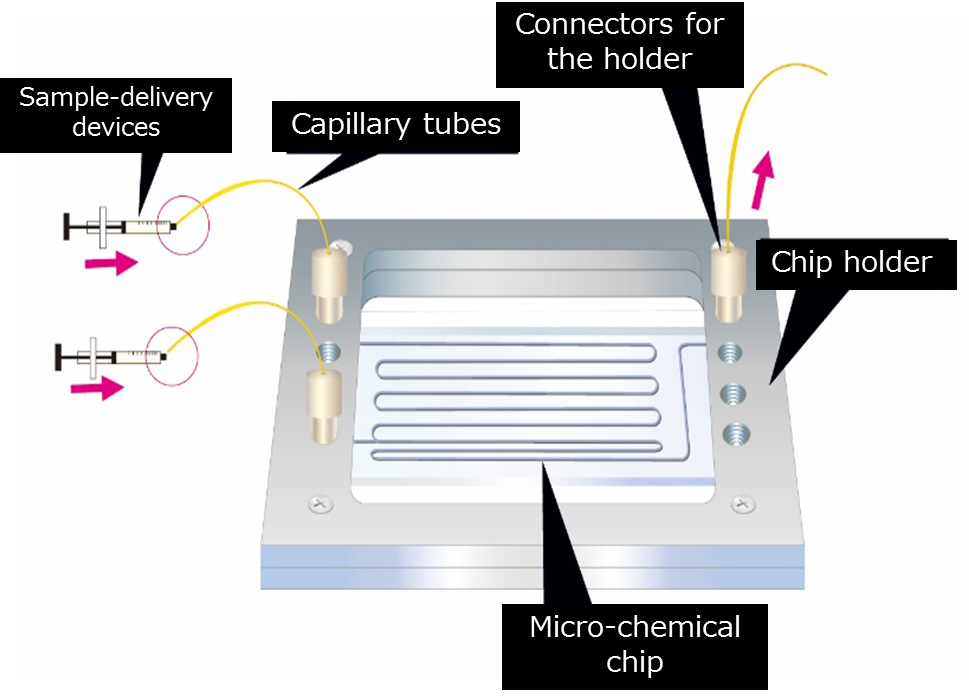
Figure: Experiment on a Chip
The following devices may optionally be used:
6, A flow meter
7, Valves
8, A temperature controller
9, An imager
10, A detector
This technical note describes how to select the material for component 1, the micro-chemical chip.
-
IMT offers two lines of micro-chemical chips, standard and custom-made ones. For the standard chips, borosilicate glass materials, such as Pyrex, are the only option. For the custom-made chips, you have three options to choose from: borosilicate glass, fused quartz, and PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane). The following describes the features of each material.
-
1. Borosilicate glass
Features
As typified by Corning's Pyrex, borosilicate glass is highly resistant to heat and chemicals. It is the most popular choice of material for custom-made micro-chemical chips.
Optical characteristics
Borosilicate glass (2 mm thick) exhibits a high transmittance of approximately 90% over the wavelength range from about 350 nm to about 2500 nm.
Applicable working processes
Wet etching and machining are used. Wet etching is common when the intended aspect ratio is about 2:1 or higher and the intended depth is between 1 and 150 μm. Machining is selected primarily when the intended aspect ratio is higher than can be achieved by wet etching.
Working accuracy
For both wet etching and machining, Dimension tolerance of up to approximately 10% occur.
-
2. Fused quartz
Features
Because of its superior optical characteristics, fused quartz is suitable for experiments using an optical system. The ranges of depths that can be achieved by wet etching are, however, narrow when compared with those with borosilicate glass. Furthermore, quartz chips are costly to produce.
Optical characteristics
Fused quartz exhibits an extremely high transmittance of approximately 90% even in the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) range, down to about 175 nm.
Applicable working processes
Wet etching and machining are used. Wet etching is common when the intended aspect ratio is about 2:1 or higher and the intended depth is between 1 and 50 m. Machining is selected primarily when the intended aspect ratio is higher than can be achieved by wet etching.
Working accuracy
For both wet etching and machining, Dimension tolerance of up to approximately 10% occur.
-
3. PDMS
Features
Produced by molding using simple molds, PDMS chips are less costly than other chips in terms of cost per chip. The material is elastic, but the surfaces are hydrophobic and less resistant to chemicals and nonspecific adsorption than those of glass chips. PDMS chips are also highly permeable to gases and should be used carefully in experiments.
Optical characteristics
The optical characteristics of PDMS are similar to those of borosilicate glass.
Applicable working processes
PDMS chips are produced by molding using simple molds and are less costly than glass chips when the cost per chip is compared.
Working accuracy
Dimension tolerance of up to approximately 20% occur.